Smart Door Locks A Comprehensive Guide
Smart Door Locks are revolutionizing home security, offering convenience and advanced features beyond traditional locks. This guide delves into the various types of smart locks available, exploring their mechanisms, security protocols, and integration capabilities within the broader smart home ecosystem. We’ll examine the installation process, address common troubleshooting issues, and discuss future trends shaping this rapidly evolving technology. Understanding the benefits and potential vulnerabilities is key to making an informed decision about securing your home with this innovative technology.
From keypad entry to fingerprint scanning and smartphone app control, the options are diverse and cater to various needs and budgets. This exploration will equip you with the knowledge to choose the best smart lock for your home, ensuring both security and user-friendliness.
Types of Smart Door Locks
Smart door locks offer a convenient and increasingly secure alternative to traditional key-based systems. They integrate technology to enhance accessibility and security, providing homeowners with a range of options to suit their needs and budget. This section explores the different types of smart locks available, comparing their features, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Smart Lock Mechanisms Comparison
Choosing the right smart lock depends on individual preferences and security requirements. Several mechanisms are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The following table provides a comparative overview.
| Feature | Keypad | Fingerprint | Smartphone App | Keycard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Numeric code entry | Biometric fingerprint scan | Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connection to a smartphone | RFID card swipe |
| Security Level | Moderate (vulnerable to brute-force attacks if weak codes are used) | High (difficult to replicate fingerprints) | High (dependent on app security and device security) | Moderate (cards can be cloned, though modern systems mitigate this risk) |
| Ease of Use | Simple, but requires remembering a code | Convenient, but requires clean and dry fingers | Convenient, but requires a charged smartphone and internet connectivity (for some models) | Convenient, but requires carrying a card |
| Price Range | $50 – $150 | $100 – $300 | $100 – $300+ (depending on features and brand) | $75 – $200 |
| Pros | Affordable, simple to install | Highly secure, no need to remember codes | Remote access, keyless entry, integration with smart home systems | Convenient, less prone to code forgetting |
| Cons | Susceptible to brute-force attacks, code sharing concerns | Can be affected by dirt or damage to the sensor | Reliance on technology and internet connectivity | Cards can be lost or stolen |
Internal Components of a Typical Smart Lock
A typical smart lock contains several key components working in concert to provide secure and convenient access. Understanding these components helps appreciate the technology involved.Imagine a cross-section diagram of a smart lock installed on a door. The outer visible part is the keypad or fingerprint scanner (depending on the type). Behind this, a small circuit board houses the microcontroller, which is the “brain” of the lock.
This receives signals from the keypad/scanner and processes them. Connected to the microcontroller is a motor that drives the locking mechanism, often a bolt that extends and retracts to secure the door. A battery compartment provides power to the system. For smart locks with app connectivity, a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi module is integrated, allowing communication with a smartphone.
Finally, the lock is mechanically linked to the door’s latch and strike plate for physical security. The internal components are usually housed within a robust metal casing for protection.
Smart Lock Security Features
Smart locks offer a convenient way to manage access to your home, but their security is paramount. High-end models incorporate sophisticated features to protect against unauthorized entry and data breaches, while understanding potential vulnerabilities is crucial for mitigating risks. This section details the security features of smart locks, their vulnerabilities, and methods to enhance overall security.Advanced Security Features in High-End Smart Locks enhance protection against unauthorized access through several key mechanisms.
These features go beyond basic password protection, offering multi-layered security.
Advanced Encryption Methods, Smart Door Locks
High-end smart locks often utilize robust encryption algorithms, such as AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with 256-bit key), to protect communication between the lock, the user’s device, and the cloud (if applicable). AES-256 is considered a highly secure encryption standard, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to decipher transmitted data, even with significant computational power. This protects against eavesdropping attacks where an attacker tries to intercept communication between the lock and its controller.
Smart door locks offer both convenience and a sleek aesthetic, seamlessly integrating into a variety of home styles. Their minimalist designs often complement the clean lines favored in Modern Interior Design , enhancing the overall sophistication of a space. Ultimately, choosing the right smart lock can significantly elevate the modern feel of your home’s security features.
Other strong encryption methods, like RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), might be used for key exchange to establish secure communication channels. The effectiveness of the encryption depends not only on the algorithm itself but also on the implementation and key management practices.
Biometric Authentication
Many advanced smart locks incorporate biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition. Fingerprint scanners use advanced algorithms to accurately match fingerprints against a registered template, while facial recognition systems utilize sophisticated image processing techniques to verify identity. This adds an extra layer of security beyond PIN codes or passwords, as biometric data is unique to each individual, making it difficult to replicate or steal.
However, the security of biometric authentication relies on the accuracy and robustness of the biometric sensor and the associated algorithms. Compromise of the biometric data storage system would still pose a significant threat.
Tamper Detection
High-end smart locks frequently include tamper detection sensors that trigger alerts if someone attempts to force the lock open, pry it off the door, or otherwise damage it. These sensors can detect unusual movements or vibrations, immediately notifying the user and potentially law enforcement through integration with security systems. This proactive measure deters physical attacks and provides immediate awareness of potential threats.
Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
While smart locks offer significant security advantages, they are not invulnerable. Understanding potential vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is crucial.
Vulnerability to Brute-Force Attacks
Locks relying solely on PIN codes are vulnerable to brute-force attacks, where an attacker systematically tries different combinations until the correct code is found. Mitigation involves implementing measures such as limiting the number of incorrect attempts before the lock temporarily disables itself or implementing a delay between attempts. Strong, complex PIN codes also significantly increase the time it takes to crack the code.
Vulnerability to Hacking
Smart locks communicating wirelessly are susceptible to hacking attempts if the communication protocols are not secure. Mitigation involves using strong encryption, regularly updating firmware, and employing strong passwords or two-factor authentication. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a one-time code sent to the user’s phone, in addition to a password.
Vulnerability to Phishing Attacks
Users can be tricked into revealing their credentials through phishing attacks, where malicious actors impersonate legitimate entities to gain access to sensitive information. Mitigation involves being cautious about suspicious emails or messages, verifying the identity of websites before entering credentials, and educating oneself about common phishing tactics.
Smart door locks offer a significant upgrade to home security, enhancing convenience and peace of mind. Integrating such technology seamlessly into your home is a key aspect of modernizing your living space, which is why considering a comprehensive Home Interior Makeover might be beneficial. A stylish new lock can truly complement a refreshed interior, tying together the enhanced security and aesthetic appeal of your updated home.
Comparison of Encryption Methods
Different smart locks employ various encryption methods, each with varying levels of security. AES-256, as mentioned earlier, is considered a highly secure option. Other methods, such as RSA, are commonly used for key exchange, ensuring secure communication channels. The choice of encryption method impacts the overall security of the smart lock, with stronger algorithms offering better protection against unauthorized access.
However, the implementation of the encryption method is equally critical. Weak implementations of even strong algorithms can render them ineffective.
Smart Lock Integration and Compatibility
Smart locks offer seamless integration with various smart home ecosystems, enhancing convenience and security. This integration allows for centralized control, automation, and enhanced user experiences, transforming your home into a truly connected environment. Understanding the compatibility options and communication protocols is crucial for choosing the right smart lock for your specific needs.Smart locks typically integrate with popular smart home platforms through various communication protocols, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Smart door locks offer enhanced security and convenience for any building. Their integration into a space’s overall design is crucial, especially when considering the broader aspects of Commercial Interior Design , which prioritizes both functionality and aesthetics. Therefore, choosing the right smart lock can significantly elevate the overall impression of a commercial space, contributing to a secure and modern feel.
These integrations allow for remote control, automation, and integration with other smart home devices.
Smart Lock Integration with Smart Home Platforms
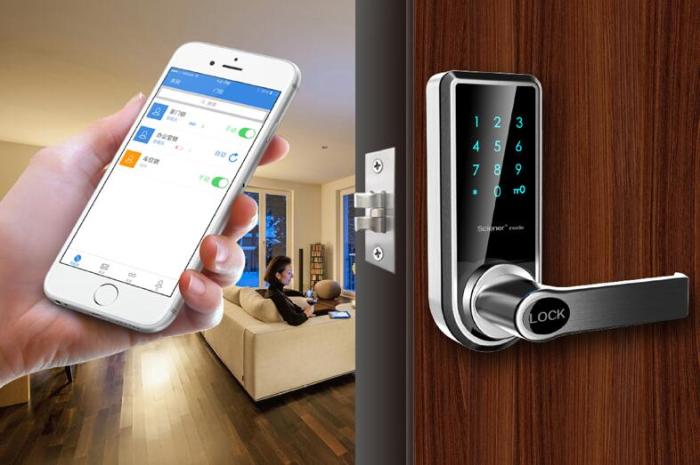
Many smart locks are compatible with popular platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit. This compatibility allows users to control their locks using voice commands, integrate them into automated routines, and manage them through a central smart home app. For instance, you could use your voice to unlock your door upon arriving home, or schedule the lock to automatically engage at a specific time.
Integration with these platforms greatly simplifies the user experience and expands the functionalities of the smart lock beyond simple keyless entry.
Smart Lock Communication Protocols
Smart locks utilize various communication protocols to connect to the internet and other smart home devices. The choice of protocol often influences the lock’s range, security, and compatibility with other devices.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi enabled smart locks offer a wide range and direct internet connectivity, allowing for remote access and control from anywhere with an internet connection. However, Wi-Fi can be more susceptible to hacking if not properly secured and requires a stable internet connection for reliable operation.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth smart locks offer a shorter range but typically consume less power and are easier to set up. They usually require a nearby smartphone or tablet for control. The shorter range is a disadvantage if you want remote access from outside your home’s Wi-Fi range.
- Z-Wave: Z-Wave is a mesh networking protocol that offers greater range and reliability than Bluetooth. It’s often used in more extensive smart home setups, allowing for communication between multiple devices without requiring a direct connection to a central hub. However, Z-Wave devices might require a dedicated Z-Wave hub for full functionality.
Integrating a Smart Lock with a Smart Home Ecosystem: A Flowchart
The process of integrating a smart lock with a smart home ecosystem, such as Amazon Alexa, generally follows these steps:(Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Choose a compatible smart lock and smart home platform.” This would branch to “Download the smart lock app and the smart home app.” Then it would lead to “Connect the smart lock to your home’s Wi-Fi network (if applicable).” Next, the flowchart would show “Link the smart lock app to your chosen smart home platform account (e.g., Amazon Alexa).” Finally, it would conclude with “Test the integration by using voice commands or the smart home app to control the lock.”)
Installation and Maintenance of Smart Locks
Installing a smart lock can seem daunting, but with careful planning and the right tools, it’s a manageable DIY project for many homeowners. Proper installation ensures both security and optimal functionality, while regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your smart lock and prevents potential problems. This section details the process of installation and provides guidance on maintaining your smart lock for years of reliable service.
Smart Lock Installation Steps
Successful smart lock installation hinges on following a precise procedure. Incorrect installation can compromise security and functionality. Always refer to your specific smart lock’s instructions, as steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
- Preparation: Gather necessary tools (screwdrivers – Phillips and flathead, possibly a drill with appropriate bits, measuring tape, pencil), consult your smart lock’s manual for specific requirements, and ensure the power is off to any connected electrical components.
- Removing the Old Lock: Carefully remove your existing door lockset according to its instructions. Take note of the placement of screws and components for reassembly if needed. This often involves removing screws from the inside and outside of the door.
- Installing the Smart Lock Mechanism: Position the smart lock’s internal mechanism within the door, aligning it with the existing holes or creating new ones as necessary (using caution to avoid damaging the door). Securely fasten all screws. This usually involves inserting the internal mechanism and securing it with screws from the inside of the door.
- Attaching the Exterior Plate: Attach the exterior plate (containing the keypad or fingerprint scanner) to the outside of the door, ensuring alignment and secure fastening. This step involves aligning the exterior plate with the internal mechanism and tightening the securing screws.
- Connecting the Internal Components: Connect the internal components of the smart lock to the internal mechanism and securely fasten any additional parts. This may involve connecting wires or engaging locking mechanisms.
- Testing and Calibration: Test the lock’s functionality thoroughly. This includes testing the keypad, fingerprint scanner (if applicable), key operation, and the overall locking and unlocking mechanisms. Some smart locks require calibration after installation.
- Pairing with the App: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to pair the smart lock with its corresponding mobile application. This involves downloading the app and following the on-screen prompts to connect your phone to the smart lock via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Troubleshooting Smart Lock Installation
During installation, several issues might arise. Understanding common problems and their solutions will streamline the process.
- Incorrect Alignment: If the lock mechanism doesn’t align correctly, carefully readjust the position of the internal components before tightening screws. Double-check your measurements and ensure everything is aligned according to the instructions.
- Strikes Plate Issues: If the door doesn’t latch properly, adjust the strike plate position. This might require slight adjustments to the strike plate’s placement to ensure a smooth latching action.
- Connectivity Problems: If the smart lock doesn’t connect to your Wi-Fi network, check your router’s settings, ensure the lock is within range, and verify the correct Wi-Fi password is entered in the app. Restart both the lock and your router if necessary.
- Dead Battery: If the lock isn’t functioning, check the batteries. Replace them with fresh batteries of the correct type and voltage as specified in the manual.
Smart Lock Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and security. A simple schedule can significantly extend the life of your smart lock.
- Monthly Check: Inspect the lock for any signs of wear and tear, loose screws, or damage. Check the battery levels and replace them if necessary.
- Quarterly Check: Lubricate moving parts with a silicone-based lubricant (as recommended by the manufacturer). This ensures smooth operation and prevents jamming.
- Annual Check: Perform a thorough inspection, checking all components and connections. Consider professional servicing if needed.
Smart Lock Market Trends and Future Developments
The smart lock market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for enhanced security and convenience. Technological advancements and a broadening range of applications are shaping the future of this dynamic sector. We can expect to see significant shifts in both the features offered and the environments where smart locks are implemented.The convergence of several technological trends is significantly impacting the development of smart locks.
These advancements are leading to more secure, user-friendly, and versatile locking systems.
Biometric Authentication Advancements
Biometric authentication is rapidly becoming a standard feature in smart locks, moving beyond simple fingerprint scanners. We are seeing the integration of more sophisticated technologies like facial recognition, voice recognition, and even vein scanning. Facial recognition, for instance, offers a contactless and convenient alternative to fingerprint scanning, while vein scanning provides an exceptionally high level of security due to its unique physiological characteristics.
These advancements enhance security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access through stolen keys or compromised codes. For example, the integration of multi-factor authentication, combining fingerprint scanning with a PIN code, creates a robust security system.
Smart door locks offer enhanced security and convenience for modern offices. Their integration into a well-designed workspace is crucial, and choosing the right lock complements the overall aesthetic. For inspiration on creating a stylish and secure office environment, consider exploring the latest trends in Office Interior Design , which can help you seamlessly blend smart technology with your office’s visual appeal.
Ultimately, the selection of smart door locks should align with your office’s design philosophy for a cohesive and functional space.
Improved Security Protocols
Beyond biometric authentication, improvements in security protocols are crucial. The use of end-to-end encryption is becoming increasingly prevalent, ensuring that communication between the smart lock and the user’s device remains private and secure. Furthermore, the development of more resilient algorithms and protocols makes smart locks less vulnerable to hacking attempts. Blockchain technology, for example, is being explored to enhance the security and transparency of smart lock systems, making them even more resistant to unauthorized access.
This is particularly relevant for high-security applications.
Expansion Beyond Residential Use
The application of smart locks extends far beyond residential settings. Commercial buildings are increasingly adopting smart lock systems for improved access control and security management. Office spaces can utilize smart locks to manage employee access, while hotels can streamline guest check-in and check-out processes. In industrial settings, smart locks play a critical role in securing sensitive equipment and materials, improving inventory management and overall security.
Smart locks are also being integrated into smart city initiatives, offering enhanced security for public infrastructure and transportation systems. For example, a large logistics company might use smart locks on delivery trucks to track and control access to sensitive packages, improving delivery efficiency and security.
Key Features Defining Smart Locks in the Next Five Years
Predicting the future is always challenging, but based on current trends, several key features will likely define smart locks within the next five years. We anticipate a rise in AI-powered features, such as predictive maintenance and automated access control based on user behavior and location. Integration with other smart home devices and ecosystems will also become more seamless.
Smart door locks offer enhanced security and convenience for modern homes. Their sleek designs can seamlessly integrate into various interior styles, even complementing a sophisticated kitchen design, such as those showcased on this website dedicated to Kitchen Interior Design. Ultimately, the choice of smart lock often reflects the overall aesthetic of the home, enhancing both security and the overall design scheme.
The development of more energy-efficient smart locks, perhaps powered by harvesting ambient energy, is also a likely development. Furthermore, we anticipate a stronger emphasis on user privacy and data security, with greater transparency and control over data collection and usage. For instance, imagine a smart lock that learns your typical arrival time and automatically unlocks the door just as you approach, while simultaneously notifying you of any unusual activity detected near your property.
Smart Lock User Experience and Accessibility
Smart locks offer convenience and security, but their usability must extend to all users, regardless of ability. A truly inclusive design considers the needs of individuals with disabilities, ensuring that everyone can benefit from the technology. This section examines the user experience of smart locks, particularly for visually impaired individuals, and explores design considerations for improved accessibility.The user experience of a smart lock for a visually impaired individual hinges on effective haptic feedback, clear audio cues, and intuitive control interfaces.
Imagine a scenario where a visually impaired person approaches their door. Instead of relying on visual cues, they depend on tactile feedback from the lock itself and audible instructions from a connected device. A poorly designed system could be frustrating and even unsafe, leading to difficulties in accessing their home. Conversely, a well-designed system would seamlessly integrate auditory and tactile feedback to guide the user through the unlocking process.
Smart Lock Design for Visual Impairment
Accessible smart lock design necessitates several key features. Firstly, the lock itself should incorporate clear and distinct tactile markings, such as raised buttons or textured surfaces, to easily identify different functionalities. These tactile cues should be strategically placed and sized to be easily manipulated by fingers of varying dexterity. Secondly, the accompanying app should offer robust voice control and clear audio feedback, guiding the user through each step of the unlocking process.
This audio feedback should be distinct and easily discernible, avoiding ambiguous or overlapping sounds. Finally, the lock’s physical design should be considered; for example, a consistently shaped and sized keypad simplifies memorization of button placement.
Examples of Accessible Smart Lock Features
Several smart locks are incorporating accessibility features. Some models feature large, clearly labeled buttons with raised tactile indicators. These buttons provide distinct feedback when pressed, confirming the user’s input. Other smart locks offer detailed voice guidance during the unlocking process, providing clear instructions on each step. Furthermore, some manufacturers are integrating Braille labels into their smart lock designs, enabling visually impaired users to independently identify and interact with the lock’s controls.
The integration of Bluetooth beacons could also aid visually impaired users in locating their smart locks more easily.
Improving Smart Lock Accessibility for Other Disabilities
Beyond visual impairments, accessible smart lock design must consider other disabilities. For individuals with limited dexterity, larger buttons, simpler interfaces, and voice control options are crucial. Smart locks should be designed to be operable with one hand, or with assistive devices. For users with cognitive impairments, clear, concise instructions and visual cues (where appropriate) are essential. Consideration should also be given to users with hearing impairments; the integration of visual alerts alongside audio cues is important.
The implementation of alternative input methods such as swipe gestures, in addition to traditional button presses, would further broaden the accessibility of smart locks.
Final Wrap-Up: Smart Door Locks

Source: org.in
Smart door locks represent a significant advancement in home security and convenience, offering a blend of technology and accessibility. While security considerations and potential vulnerabilities must be addressed, the overall benefits of enhanced protection and remote access make them a compelling choice for modern homeowners. As technology continues to evolve, expect even greater integration with smart home ecosystems and increasingly sophisticated security features, further solidifying the smart lock’s position as a cornerstone of modern home security.
FAQ Section
What happens if my smart lock’s battery dies?
Most smart locks have a backup power source, usually a 9V battery connection, allowing you to unlock the door even with a depleted internal battery.
Can I still use a physical key with a smart lock?
Many smart locks offer the option of using a physical key as a backup, providing peace of mind in case of technical issues or power outages.
Are smart locks difficult to install?
Installation difficulty varies depending on the lock type and your existing door hardware. However, many smart locks are designed for DIY installation with clear instructions.
How secure are smart locks against hacking?
High-quality smart locks employ robust encryption and security protocols to protect against unauthorized access. Regular software updates and strong passwords are crucial for maintaining security.
What if I lose my smartphone or forget my PIN?
Most smart locks provide methods for recovering access, such as using a physical key or contacting the manufacturer for assistance.