How to Start a Cryptocurrency Business
How to start a cryptocurrency business is a question on many minds, fueled by the exciting potential and inherent risks of this rapidly evolving industry. This guide navigates the complexities of launching a successful cryptocurrency venture, from understanding the diverse cryptocurrency landscape and regulatory hurdles to crafting a robust business plan and building a secure platform. We will explore various business models, crucial legal considerations, effective marketing strategies, and the essential operational aspects for long-term growth and sustainability.
This comprehensive approach aims to equip aspiring entrepreneurs with the knowledge and insights needed to confidently embark on this challenging yet potentially rewarding journey.
The cryptocurrency market presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges. This guide will dissect the intricacies of various blockchain platforms, analyze successful and failed business models, and provide practical advice on navigating the legal and regulatory frameworks governing cryptocurrency operations in different jurisdictions. We will delve into creating a compelling business plan, securing funding, and building a user-friendly and secure platform (where applicable).
Finally, we’ll explore effective marketing and customer acquisition strategies to establish a strong market presence and ensure sustainable growth.
Understanding the Cryptocurrency Landscape: How To Start A Cryptocurrency Business
Launching a successful cryptocurrency business requires a thorough understanding of the complex and ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape. This involves familiarity with various cryptocurrency types, the regulatory frameworks governing their use, suitable blockchain platforms, and the successes and failures of existing businesses in the space. A comprehensive grasp of these elements is crucial for strategic planning and risk mitigation.
Types of Cryptocurrencies and Underlying Technologies
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual assets designed to work as a medium of exchange. They utilize cryptography to secure and verify transactions as well as to control the creation of new units of a particular cryptocurrency. Different cryptocurrencies employ diverse underlying technologies and possess varying characteristics. Bitcoin, for instance, utilizes a proof-of-work consensus mechanism, requiring significant computational power to validate transactions and secure the network.
This contrasts with Ethereum, which employs a proof-of-stake mechanism, offering potentially greater energy efficiency. Other cryptocurrencies, like stablecoins (e.g., Tether, USD Coin), aim to maintain a stable value pegged to a fiat currency or other assets, mitigating the volatility often associated with cryptocurrencies. The choice of cryptocurrency will significantly influence the business model and technological infrastructure required.
Regulatory Environment Surrounding Cryptocurrency Businesses
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency businesses is fragmented and varies significantly across jurisdictions. Some countries have embraced a relatively permissive approach, providing clear guidelines and licensing frameworks for cryptocurrency exchanges and related services. Others maintain a more cautious stance, implementing stricter regulations or outright bans. For example, Singapore has established a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrency service providers, while China has banned cryptocurrency trading and mining activities.
Understanding the specific legal and regulatory requirements in the target market is essential for compliance and operational viability. Businesses must carefully navigate issues like anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, which are increasingly stringent globally.
Launching a cryptocurrency business requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing legal compliance and a strong understanding of market trends. Understanding the entrepreneurial spirit, often associated with American culture , can be beneficial in navigating the challenges and seizing opportunities within this dynamic sector. Ultimately, success hinges on a well-defined business plan and a commitment to adapting to the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
Comparison of Blockchain Platforms
Various blockchain platforms offer distinct features and functionalities relevant to cryptocurrency businesses. Ethereum, with its smart contract capabilities, is popular for decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects. Other platforms, such as Solana and Cardano, focus on scalability and transaction speed, addressing some of Ethereum’s limitations. The choice of blockchain platform depends on the specific needs of the cryptocurrency business, considering factors such as transaction costs, scalability, security, and the availability of developer tools and community support.
A detailed comparison of these platforms, considering factors such as transaction speed, security, and cost, is critical for informed decision-making.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Cryptocurrency Businesses
Analyzing the strategies of successful and unsuccessful cryptocurrency businesses offers valuable insights. Coinbase, a publicly traded cryptocurrency exchange, has achieved significant success by focusing on user-friendliness, regulatory compliance, and a diverse range of services. Conversely, the collapse of FTX, a once prominent cryptocurrency exchange, highlights the risks associated with inadequate risk management, lack of transparency, and regulatory non-compliance.
Studying these case studies, noting both successes and failures, provides crucial lessons in building a sustainable and resilient cryptocurrency business. The strategies employed, the challenges faced, and the outcomes achieved offer valuable learning opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs.
Defining Your Cryptocurrency Business Model
Choosing the right business model is crucial for success in the dynamic cryptocurrency landscape. A well-defined model Artikels your revenue streams, target audience, and operational strategies, guiding your venture towards profitability and sustainability. This section will explore three distinct cryptocurrency business models, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, risks, and mitigation strategies.
Starting a cryptocurrency business requires careful planning and understanding of the market. A strong business plan is crucial, and considering the skills needed, it’s helpful to research current employment trends, such as those highlighted in this article on Most popular jobs in the USA , to identify potential talent pools and market demands. This research can inform your hiring strategy and overall business development in the competitive cryptocurrency sector.
Cryptocurrency Exchange
A cryptocurrency exchange acts as an intermediary, facilitating the buying, selling, and trading of various cryptocurrencies. Revenue is primarily generated through trading fees, which are typically a percentage of each transaction. The target audience includes both individual investors and institutional traders seeking access to a diverse range of crypto assets.
- Advantages: High potential for revenue generation with high trading volume, relatively low barrier to entry compared to other models (depending on the scale and features offered), potential for diversification through listing multiple cryptocurrencies.
- Disadvantages: High regulatory scrutiny and compliance costs, vulnerability to security breaches and hacking attempts, intense competition from established exchanges.
- Risks: Security breaches leading to loss of user funds, regulatory changes impacting operations, market volatility impacting trading volume and profitability.
- Mitigation Strategies: Implementing robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication and cold storage, proactive compliance with relevant regulations, diversifying revenue streams beyond trading fees (e.g., offering staking services).
Cryptocurrency Mining
Cryptocurrency mining involves using specialized hardware to solve complex mathematical problems, validating transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain. Revenue is generated through the newly minted cryptocurrency received as a reward for successfully mining a block, as well as transaction fees. The target audience for this model is less directly consumer-focused; it’s primarily driven by technical expertise and access to resources.
- Advantages: Potential for high returns if mining is successful and energy costs are low, relatively low barrier to entry for smaller-scale operations (though large-scale operations require significant investment), direct participation in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
- Disadvantages: High initial investment in specialized hardware, significant energy consumption and associated costs, intense competition from larger mining pools, potential for obsolescence of mining hardware.
- Risks: Hardware failure, fluctuating cryptocurrency prices impacting profitability, increased difficulty of mining reducing rewards, regulatory changes affecting mining operations.
- Mitigation Strategies: Investing in energy-efficient hardware, joining a mining pool to increase chances of block rewards, diversifying mining operations across different cryptocurrencies, hedging against price volatility.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platform
A DeFi platform offers various financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, built on blockchain technology. Revenue streams can include transaction fees, interest earned on lending, and platform usage fees. The target audience comprises individuals and institutions seeking decentralized financial services, often attracted by the potential for higher yields and greater transparency.
- Advantages: High potential for growth in the rapidly expanding DeFi market, potential for innovative financial products and services, greater transparency and accessibility compared to traditional finance.
- Disadvantages: Complex development and maintenance requirements, high security risks due to smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty in the evolving DeFi space.
- Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities leading to exploits and losses, regulatory changes impacting platform operations, market volatility affecting user participation and profitability.
- Mitigation Strategies: Thorough smart contract audits, robust security measures to prevent exploits, proactive engagement with regulators to ensure compliance, diversification of revenue streams.
SWOT Analysis: Cryptocurrency Exchange
| Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|
| High potential for revenue generation through trading fees. | High regulatory scrutiny and compliance costs. |
| Access to a large and diverse user base. | Vulnerability to security breaches and hacking attempts. |
| Potential for diversification through listing multiple cryptocurrencies. | Intense competition from established exchanges. |
| Opportunity | Threat |
| Expansion into new geographic markets. | Market volatility impacting trading volume and profitability. |
| Development of innovative trading features and tools. | Regulatory changes impacting operations. |
| Integration with other DeFi platforms. | Emergence of new technologies and competitors. |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for any cryptocurrency business. The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrencies is complex and varies significantly by jurisdiction. Failure to comply with applicable laws can lead to severe penalties, including hefty fines, business closure, and even criminal prosecution. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for the long-term success and sustainability of your venture.
Legal Requirements for Cryptocurrency Businesses in the United States
The United States lacks a single, comprehensive federal law governing cryptocurrencies. Instead, regulation is fragmented across various agencies, including the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). This necessitates a multifaceted approach to legal compliance. The specific requirements depend heavily on the nature of your cryptocurrency business.
For example, a cryptocurrency exchange faces a different set of regulations than a company offering cryptocurrency-related software.
- State Money Transmitter Licenses: Many states require money transmitter licenses for businesses facilitating the exchange of cryptocurrency for fiat currency or other digital assets. The licensing process varies by state, involving background checks, financial audits, and detailed business plans.
- Federal Registration with FinCEN: Businesses acting as money transmitters must register with FinCEN as Money Services Businesses (MSBs) and comply with AML and KYC regulations.
- SEC Compliance (for Securities Offerings): If your business involves the offering or sale of cryptocurrencies deemed to be securities, you must comply with the SEC’s rigorous registration and disclosure requirements under the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
- CFTC Compliance (for Derivatives): If your business involves the trading of cryptocurrency derivatives, you’ll need to adhere to the regulations of the CFTC.
- State and Federal Tax Obligations: Cryptocurrency transactions are subject to various taxes at both the state and federal levels, including capital gains taxes and income taxes. Accurate record-keeping and timely tax filings are essential.
Obtaining Necessary Licenses and Permits
The process of obtaining the necessary licenses and permits is often lengthy and complex. It generally involves submitting detailed applications, undergoing background checks, providing financial information, and demonstrating compliance with relevant regulations. The specific requirements vary depending on the type of license or permit and the state or federal agency involved. Seeking legal counsel specializing in cryptocurrency regulation is highly recommended to navigate this process effectively.
For example, obtaining a money transmitter license might involve submitting a comprehensive business plan, undergoing a thorough background check of key personnel, and demonstrating sufficient financial resources to cover operational expenses and potential liabilities.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations
AML and KYC regulations are designed to prevent the use of cryptocurrencies for illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. These regulations require businesses to verify the identities of their customers and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Failure to comply with AML and KYC regulations can result in significant penalties. For example, businesses must implement robust customer due diligence procedures, including verifying customer identities using government-issued identification documents and conducting enhanced due diligence for high-risk customers.
Launching a cryptocurrency business requires careful planning and understanding of market trends. For instance, consider the innovative sponsorship models used by American sports leagues , which could offer valuable insights into attracting investors and building brand recognition. Applying similar strategies to build a strong community and secure partnerships is crucial for success in the competitive cryptocurrency landscape.
Transaction monitoring systems are also crucial for identifying potentially suspicious activity.
Compliance Best Practices for a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Cryptocurrency exchanges are subject to particularly stringent AML and KYC regulations due to their role in facilitating large-scale cryptocurrency transactions. Best practices include:
- Robust KYC/AML Program: Implementing a comprehensive program that includes thorough customer identification, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting.
- Independent Audits: Regularly conducting independent audits to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
- Employee Training: Providing regular training to employees on AML/KYC procedures and best practices.
- Secure Data Storage: Implementing robust security measures to protect customer data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Geographic Restrictions: Restricting services to jurisdictions where the exchange is properly licensed and compliant.
Developing Your Cryptocurrency Business Plan
A robust business plan is crucial for the success of any cryptocurrency venture. It serves as a roadmap, guiding your operations and attracting potential investors. This plan should be comprehensive, detailing your company’s vision, strategies, and financial projections, ultimately demonstrating the viability and potential of your cryptocurrency business. A well-structured plan increases your chances of securing funding and navigating the complexities of the cryptocurrency market.A comprehensive business plan should encompass several key elements, allowing you to articulate your vision and strategy clearly to potential investors and partners.
These elements work together to create a compelling narrative for your business.
Company Mission, Vision, and Goals, How to start a cryptocurrency business
The mission statement defines your company’s core purpose and reason for existence within the cryptocurrency landscape. For example, a mission statement might be “To provide secure and accessible decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions to underserved communities.” The vision statement articulates your long-term aspirations, painting a picture of your company’s future success. A vision statement might be “To become the leading provider of user-friendly DeFi tools, empowering financial inclusion globally.” Finally, clearly defined, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals provide concrete milestones to track progress.
These goals might include specific user acquisition targets, revenue projections, or technological advancements.
Financial Projections
Developing realistic financial projections for the first three years is essential. This involves creating detailed revenue forecasts based on anticipated user growth, transaction fees, or other revenue streams. For example, a company launching a new cryptocurrency exchange might project transaction volume growth based on market trends and competitor analysis. Simultaneously, you need to develop a comprehensive expense budget, including operational costs, marketing expenses, technology development, and personnel salaries.
These projections should be presented in a clear and concise manner, ideally using financial modeling tools to demonstrate the potential profitability and financial health of your business. Consider including sensitivity analysis to show how your projections might change under different market conditions. For instance, a sensitivity analysis might show the impact of a 20% decrease in transaction fees on projected profitability.
Marketing Strategy
A well-defined marketing strategy is crucial for attracting customers and building brand awareness in a competitive market. This involves identifying your target audience, defining your brand identity, and selecting appropriate marketing channels. For example, a company targeting institutional investors might focus on content marketing, attending industry conferences, and building relationships with key players. In contrast, a company targeting retail investors might leverage social media marketing, influencer partnerships, and paid advertising campaigns.
The strategy should detail specific tactics, timelines, and budget allocations for each channel. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as website traffic, social media engagement, and customer acquisition cost should be defined to measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts.
Funding Acquisition Plan
Securing funding is often a critical step in launching a cryptocurrency business. Several options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Venture capital firms offer significant funding but often require a substantial equity stake. Angel investors provide early-stage funding in exchange for equity, while Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) allow you to raise capital by selling your own cryptocurrency tokens.
Your funding plan should Artikel the chosen funding strategy, the amount of capital sought, the proposed use of funds, and the terms of investment. For example, a company might Artikel a plan to raise $5 million through a combination of Series A funding from venture capitalists and a private token sale to accredited investors. It’s crucial to present a compelling investment thesis, highlighting the potential for high returns and minimizing the risks associated with your cryptocurrency venture.
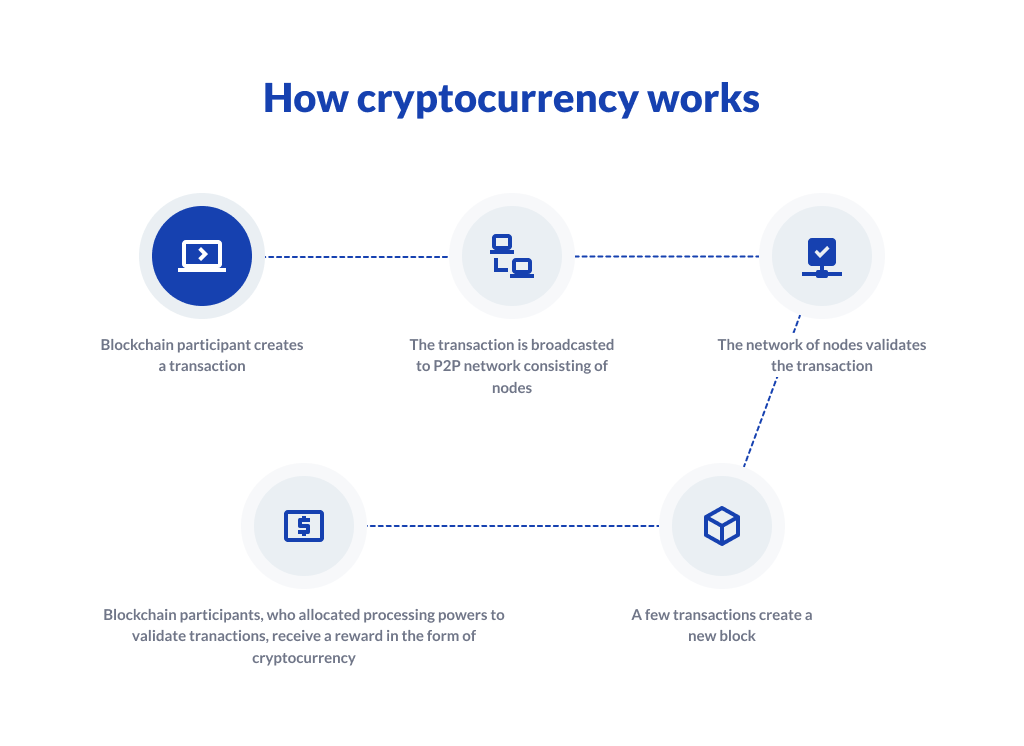
Building Your Cryptocurrency Platform (if applicable)
Source: cloudfront.net
Developing a cryptocurrency platform requires careful planning and execution. This involves designing a robust architecture, implementing stringent security measures, and selecting an appropriate technology stack. The platform’s success hinges on its ability to provide a secure, user-friendly, and efficient trading experience.
Launching a cryptocurrency business requires careful planning and research into market trends. For a successful launch, consider factors such as regulatory compliance and secure infrastructure; however, remember to take some time for yourself! Perhaps a relaxing trip to some of the Best places to visit in the USA could provide the inspiration and rejuvenation needed before diving back into the complexities of the cryptocurrency market.
After your break, you can then focus on developing a robust business strategy.
Platform Architecture Design
A cryptocurrency trading platform’s architecture should prioritize scalability, security, and performance. A typical architecture would include a front-end (user interface), a back-end (server-side logic and data processing), and a database to store user data and transaction history. The front-end would handle user interactions, while the back-end would manage order execution, matching, and account management. The database would need to be highly reliable and capable of handling a large volume of transactions.
Microservices architecture is often preferred for its flexibility and scalability, allowing for independent deployment and updates of individual components. This modular approach also improves maintainability and reduces the risk of system-wide failures.
Security Measures
Protecting user assets and data is paramount. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory for all users. Cold storage for a significant portion of cryptocurrency holdings is essential to mitigate the risk of hacking. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address vulnerabilities. Data encryption both in transit and at rest is crucial.
Implementation of robust anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures are necessary to comply with regulations and prevent illicit activities. Furthermore, a comprehensive incident response plan should be in place to handle security breaches effectively. This plan should Artikel procedures for containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis.
Technology Stack
The choice of technology stack significantly impacts the platform’s performance, security, and scalability. Popular choices for the back-end include languages like Python (with frameworks such as Django or Flask) or Node.js, known for their scalability and large community support. For the database, PostgreSQL or MongoDB are often used, offering robust features and scalability. The front-end could be developed using JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, providing a responsive and user-friendly interface.
For secure communication, HTTPS is essential, and integration with established payment gateways might be necessary for fiat currency transactions.
Trading Dashboard UI Mockup
The trading dashboard is a critical component of the platform. A well-designed dashboard provides users with a clear and concise overview of their trading activity. Below is a sample table showcasing key trading information:
| Asset | Price (USD) | Quantity | Total Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTC | $28,000 | 1.2 | $33,600 |
| ETH | $1,800 | 5.0 | $9,000 |
| LTC | $80 | 100 | $8,000 |
| XRP | $0.50 | 5,000 | $2,500 |
Marketing and Customer Acquisition

Source: cryptoryancy.com
Successfully launching a cryptocurrency business requires a robust marketing strategy to attract and retain customers. This involves educating potential clients about the complexities of cryptocurrency, building brand awareness, and establishing trust. A multi-faceted approach, combining content marketing, social media engagement, and targeted advertising, is crucial for achieving significant market penetration.Effective marketing goes beyond simply advertising your services; it’s about building a community around your brand and fostering long-term relationships with customers.
Understanding your target audience and tailoring your message to their specific needs and concerns is paramount. This section will Artikel key strategies for reaching your ideal customer and converting them into loyal users.
Content Marketing Strategy
A well-defined content marketing strategy is essential for educating potential customers about cryptocurrency and the unique value proposition of your business. This strategy should encompass various content formats, including blog posts, white papers, infographics, and video tutorials, all designed to build trust and expertise. For example, a blog post explaining the benefits of using your specific cryptocurrency platform compared to competitors could attract a technically savvy audience.
A series of short, easily digestible videos demonstrating the platform’s user-friendliness could attract a wider audience. White papers detailing the technical aspects of your platform’s security and functionality could appeal to investors and developers.
Launching a cryptocurrency business requires careful planning and understanding of the market. A key aspect is identifying potential customer bases, and this often involves considering the dominant sectors of the economy; for instance, understanding the landscape of Top industries in the USA can help you target your services effectively. This market research will ultimately inform your business strategy and increase your chances of success in the competitive cryptocurrency space.
Social Media Marketing Campaign
Social media platforms offer an unparalleled opportunity to reach a wide audience and build brand awareness. A successful social media campaign requires a clear understanding of your target audience’s preferred platforms and the type of content that resonates with them. For example, if your target audience is comprised of younger investors, platforms like TikTok and Instagram might be more effective than LinkedIn.
The content should be engaging, informative, and consistent with your brand’s overall message. This could involve sharing industry news, educational content, behind-the-scenes glimpses of your company culture, and interactive polls or quizzes. Regular engagement with followers through comments and direct messages is crucial for building a strong community.
Customer Acquisition Channels
Three distinct customer acquisition channels, each with varying costs and effectiveness, are Artikeld below:
The selection of the most appropriate channels depends on your target audience, budget, and business goals. A diversified approach, utilizing a combination of these channels, is often the most effective strategy.
| Channel | Cost | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paid Advertising (Google Ads, Social Media Ads) | High (variable depending on campaign parameters) | High (potentially quick results, but requires ongoing investment) | Running targeted Google Ads campaigns focusing on s related to your cryptocurrency services, or using Facebook/Instagram ads to reach specific demographics interested in investing. |
| Content Marketing (Blog, White Papers, Educational Videos) | Medium (initial investment in content creation, ongoing optimization) | Medium to High (long-term strategy, builds brand authority and trust) | Creating high-quality blog posts, white papers, and videos that educate users about cryptocurrency and your platform, and then promoting this content organically through social media and search engine optimization (). |
| Affiliate Marketing | Medium to High (commission-based, varying rates) | Medium to High (can generate significant leads, but relies on partnerships) | Partnering with influencers or other businesses in the cryptocurrency space to promote your platform in exchange for a commission on referred customers. This requires careful selection of partners to ensure alignment with your brand values. |
Examples of Engaging Content
Engaging content is crucial for capturing the attention of potential customers. Examples of such content include:
- Blog Post: “Demystifying Cryptocurrency: A Beginner’s Guide to Investing Safely.” This blog post could explain fundamental concepts in simple terms, building trust and establishing your business as a reliable source of information.
- Social Media Update (Twitter): “Excited to announce our partnership with [Partner Company]! This collaboration will bring even more innovative features to our platform. #cryptocurrency #blockchain #partnership” This post leverages the power of partnerships to build credibility and expand reach.
- Infographic: A visually appealing infographic comparing the key features and benefits of your platform versus its competitors. This allows for quick comprehension of complex information.
Team and Operations

Source: india.com
A successful cryptocurrency business requires a well-structured team and efficient operational processes. This section Artikels the key personnel roles, operational procedures, scaling strategies, and essential tools and technologies necessary for a robust and sustainable cryptocurrency venture. Building a strong foundation in these areas is critical for navigating the complexities of the cryptocurrency market and ensuring long-term success.
Key Personnel Roles and Responsibilities
A typical cryptocurrency business needs individuals with expertise in various areas. The specific roles and responsibilities will depend on the business model and scale, but some key positions include a CEO for overall leadership and strategic direction, a CTO for technological oversight and development, a CFO for financial management and compliance, a legal counsel for regulatory compliance and risk management, and a marketing and sales team to promote the business and acquire customers.
Each role demands a unique skillset and contributes significantly to the overall success of the enterprise. For example, the CTO would be responsible for the security of the platform, the development of new features, and the overall technical architecture, while the CFO would manage the financial health of the company, ensuring compliance with regulations, and overseeing budgeting and forecasting.
Operational Processes for Managing Customer Accounts, Transactions, and Security
Robust operational processes are paramount for managing customer accounts, transactions, and security. Customer account management involves secure user registration, KYC/AML compliance (Know Your Customer/Anti-Money Laundering), and efficient account support. Transaction processing requires secure and reliable systems for handling cryptocurrency transfers, order execution, and reconciliation. Security is paramount and involves implementing multi-factor authentication, encryption, regular security audits, and robust incident response plans.
For instance, a well-designed system would automatically flag suspicious transactions and trigger alerts to the security team for immediate investigation. Failure to maintain stringent security protocols can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Scaling the Business for Future Growth
Planning for scalability is crucial for long-term growth. This involves anticipating increased transaction volume, expanding customer base, and adapting to evolving technological advancements. A scalable system should be able to handle a significant increase in user traffic and transactions without compromising performance or security. This might involve migrating to a more robust infrastructure, implementing load balancing techniques, or adopting a microservices architecture.
Examples of scaling strategies include cloud-based solutions, which provide the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand, and strategic partnerships, which can help to expand the business’s reach and capabilities. Companies like Coinbase have demonstrated successful scaling through strategic infrastructure investments and a phased approach to feature development.
Essential Tools and Technologies
Efficient operation requires a range of tools and technologies. These include secure wallets for storing cryptocurrencies, blockchain explorers for monitoring transactions, transaction monitoring systems for compliance, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems for managing customer interactions, and robust security software for protecting the platform and user data. Furthermore, data analytics tools are crucial for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and identifying areas for improvement.
The specific tools will vary based on the business model and the scale of operations, but a well-equipped technology stack is fundamental for success. For example, a company might use a distributed ledger technology (DLT) for enhanced security and transparency in transactions.
Wrap-Up
Launching a cryptocurrency business demands careful planning, meticulous execution, and a deep understanding of the dynamic cryptocurrency ecosystem. This guide has provided a framework for navigating the complexities involved, from defining a viable business model and ensuring legal compliance to developing a robust marketing strategy and building a secure platform. Remember that continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for success in this ever-evolving field.
By understanding the risks, embracing innovation, and adhering to best practices, aspiring entrepreneurs can increase their chances of building a thriving and sustainable cryptocurrency business. The journey is challenging, but the potential rewards are significant for those prepared to navigate the complexities with diligence and foresight.
Detailed FAQs
What are the initial capital requirements for starting a cryptocurrency business?
The initial capital requirements vary significantly depending on the chosen business model and scale of operations. A smaller-scale operation might require less capital than a large-scale cryptocurrency exchange.
What are the key technological skills needed for a cryptocurrency business?
Depending on the business model, skills in blockchain technology, cryptography, software development (particularly in languages like Python, Solidity, or JavaScript), database management, and cybersecurity are highly valuable.
How can I protect my cryptocurrency business from cyberattacks?
Implementing robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, regular security audits, and employing cybersecurity professionals, is crucial to protect against cyberattacks.
What are the tax implications of running a cryptocurrency business?
Tax implications vary significantly by jurisdiction. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional familiar with cryptocurrency regulations to ensure compliance with local laws.
How can I build trust and credibility with my customers?
Transparency, security measures, regulatory compliance, and positive customer reviews are vital for building trust and credibility. Demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices is also essential.