Smart Home Integration A Connected Home
Smart Home Integration represents a significant advancement in home technology, seamlessly connecting various devices and systems to enhance convenience, security, and energy efficiency. This interconnected ecosystem leverages the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to create a truly intelligent living space, adapting to the needs and preferences of its inhabitants. From automated lighting and climate control to integrated security systems and entertainment options, the possibilities are virtually limitless.
This exploration delves into the core components, integration challenges, security considerations, and future trends of smart home technology. We will examine various smart home ecosystems, comparing their strengths and weaknesses, and providing practical guidance for navigating the complexities of creating and maintaining a connected home environment.
Defining Smart Home Integration
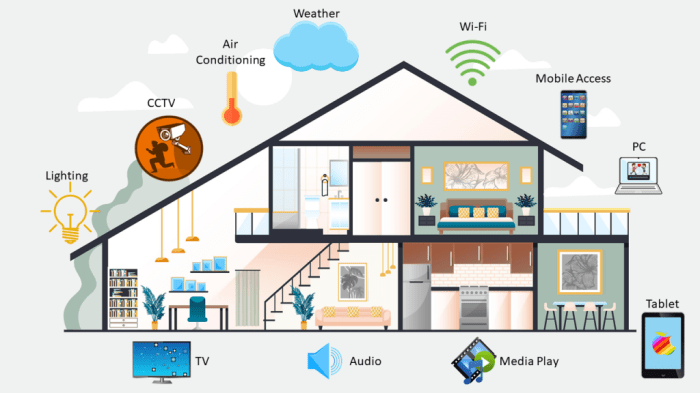
Source: co.id
Smart home integration represents the seamless connection and communication between various smart devices and systems within a home environment. This interconnectedness allows for automated control, enhanced convenience, and improved energy efficiency, ultimately creating a more comfortable and responsive living space. The core benefit lies in the ability to manage multiple devices and systems from a central point, simplifying daily routines and optimizing resource utilization.Smart home integration relies on a complex interplay of several key technologies.
Smart home integration offers incredible convenience and control over your living space. However, seamlessly blending this technology into your home’s aesthetic requires careful planning; this is where a professional Interior Design Consultation can be invaluable. A skilled designer can help integrate smart devices in a way that enhances, not detracts from, your home’s overall design, ensuring a cohesive and stylish smart home experience.
These technologies work in concert to enable the communication and control necessary for a truly integrated system.
Technologies Involved in Smart Home Integration
The foundation of smart home integration is the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT encompasses the network of physical objects—”things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These “things” range from smart thermostats and lighting systems to security cameras and appliances. Cloud computing provides the infrastructure for storing and processing the vast amounts of data generated by these interconnected devices.
This allows for remote access and control, as well as advanced analytics to optimize system performance. Artificial intelligence (AI) plays an increasingly crucial role, enabling features such as predictive maintenance, personalized automation, and voice control. AI algorithms analyze data patterns to anticipate user needs and proactively adjust settings accordingly. For example, AI might learn your preferred temperature settings and adjust the thermostat automatically based on your schedule and location.
Examples of Smart Home Ecosystems and Their Interoperability
Several major players dominate the smart home market, each offering its own ecosystem of devices and applications. Examples include Amazon’s Alexa ecosystem, Google’s Home ecosystem, and Apple’s HomeKit. While each ecosystem offers a range of devices and functionalities, their interoperability—the ability to work together seamlessly—remains a challenge. Some ecosystems are more open than others, allowing for greater compatibility with third-party devices and services.
For instance, while devices within a single ecosystem often integrate flawlessly, connecting a Philips Hue smart lighting system (typically associated with other ecosystems) to a Google Home system might require workarounds or limitations in functionality. Efforts are underway to improve interoperability through standardized protocols and open APIs, but complete seamless integration across all platforms remains an ongoing goal.
The current reality is often a mixture of seamless integration within a chosen ecosystem and more limited, potentially requiring workarounds, integration across different platforms.
Key Components of Smart Home Systems
A smart home system isn’t just a collection of gadgets; it’s a carefully orchestrated network of hardware and software working together to automate and enhance your living space. Understanding the key components is crucial to building a system that meets your needs and expectations. This section will delve into the essential hardware, the role of software, and the communication protocols that make it all work.
Smart home systems rely on a combination of physical devices and digital interfaces to achieve their functionality. The interplay between hardware, software, and communication protocols forms the backbone of a successful smart home integration.
Essential Hardware Components
Smart homes rely on a range of hardware components to sense, control, and interact with the environment. These components are interconnected and work together to create a unified system.
These components can be broadly categorized into three main groups: control interfaces, sensors, and actuators. Control interfaces, such as smart speakers and mobile apps, allow users to interact with the system. Sensors monitor various aspects of the home environment, including temperature, light, and motion. Actuators, such as smart lights and thermostats, respond to commands from the control interfaces or triggers from sensors.
- Smart Speakers: Devices like Amazon Echo or Google Home act as central control points, allowing voice commands to manage other smart devices.
- Smart Hubs: These act as central communication points, connecting various devices using different protocols. Examples include Samsung SmartThings and Philips Hue Bridge.
- Sensors: These devices monitor various environmental factors. Examples include motion sensors (detecting movement), door/window sensors (detecting openings), temperature sensors, and humidity sensors.
- Smart Plugs: These allow you to control any non-smart appliance by plugging it into the smart plug and controlling it via an app or voice command.
- Smart Lighting: These offer control over lighting intensity, color, and scheduling.
- Smart Thermostats: These learn your preferences and automatically adjust temperatures for optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
The Role of Software and Apps
The hardware components of a smart home are only half the equation. Software and dedicated apps are essential for managing and controlling these devices effectively.
Software applications provide the user interface for interacting with smart home devices. They allow users to configure settings, create automation routines, monitor device status, and receive alerts. Many apps offer centralized control, allowing users to manage all their smart home devices from a single dashboard. Robust software also plays a critical role in data security and privacy.
Smart Home Device Protocols
Different smart home devices communicate using various protocols. Understanding these protocols is crucial for ensuring compatibility within your system.
Smart home integration offers unparalleled convenience, seamlessly connecting various devices for a unified experience. A key component of this integration often involves robust home automation systems, such as those detailed on this informative website: Home Automation Systems. Understanding these systems is crucial for maximizing the potential of your smart home setup and achieving true home automation.
Ultimately, smart home integration strives to simplify daily life.
The choice of protocol can significantly impact factors such as range, power consumption, security, and compatibility. Some protocols are proprietary, meaning they only work with devices from the same manufacturer, while others are open standards, offering greater interoperability.
| Protocol Name | Range | Power Consumption | Security | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zigbee | Up to 100 meters (depending on obstacles) | Low | AES-128 encryption | Widely adopted, but not universal |
| Z-Wave | Up to 30 meters (depending on obstacles) | Low | Strong encryption | Good compatibility within the Z-Wave ecosystem |
| Wi-Fi | Varies greatly depending on router and obstacles | Moderate to High | WPA2/WPA3 encryption | Very widespread, but can be less energy efficient for battery-powered devices |
Integration Challenges and Solutions

Source: servicepower.com
Building a truly integrated smart home can present significant hurdles. The biggest challenge stems from the lack of universal standardization across different manufacturers and their respective protocols. This incompatibility often leads to frustrating interoperability issues, preventing devices from seamlessly communicating and working together as intended. Furthermore, the sheer number of devices and systems available can overwhelm even the most tech-savvy homeowner, making setup and management complex.
Interoperability Issues and Their Solutions
The most prevalent challenge in smart home integration is the lack of a single, universally accepted communication standard. Different manufacturers utilize proprietary protocols, meaning devices from various brands often struggle to communicate effectively. This incompatibility prevents seamless control and automation across the entire smart home ecosystem. For example, a smart light bulb from Company A might not work with a smart home hub from Company B, hindering the ability to control the lighting via a centralized app.Solutions to these interoperability issues frequently involve the use of universal gateways or bridges.
These devices act as translators, converting signals between different protocols, enabling communication between otherwise incompatible devices. For example, a Z-Wave to Zigbee gateway allows devices using these different wireless protocols to interact. Cloud-based platforms also play a significant role, offering centralized control and management even for devices that use different communication protocols. These platforms act as intermediaries, translating commands and data between various devices and systems.
Troubleshooting Smart Home Integration Problems
Effective troubleshooting involves a systematic approach. A step-by-step guide can significantly aid in resolving common integration issues.
- Verify Device Compatibility: Before purchasing any smart home device, carefully check its compatibility with your existing system and other devices. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications and online reviews to ensure seamless integration.
- Check Network Connectivity: Ensure all devices are connected to the same Wi-Fi network or compatible communication network. Weak Wi-Fi signals or network connectivity problems are frequent causes of integration issues. Consider using a Wi-Fi extender or mesh network for improved coverage.
- Restart Devices and Hubs: A simple reboot can often resolve minor glitches. Restart your smart home hub, router, and individual devices to clear temporary errors and refresh connections.
- Update Firmware: Outdated firmware can lead to compatibility problems. Regularly check for and install firmware updates for all your smart home devices and the central hub.
- Check Device Settings: Ensure that the settings on individual devices and within the smart home app are correctly configured. Incorrect settings, such as incorrect network passwords or incompatible modes, can hinder integration.
- Consult Manufacturer Support: If problems persist, contact the manufacturers of your devices for technical assistance. They can provide specific troubleshooting steps or identify potential compatibility issues.
Security and Privacy in Smart Home Integration
The increasing interconnectedness of smart home devices presents both exciting opportunities and significant security and privacy challenges. While the convenience of automated lighting, remote temperature control, and voice-activated assistants is undeniable, the potential for unauthorized access, data breaches, and privacy violations necessitates a thorough understanding of the risks and appropriate mitigation strategies. This section will explore the potential vulnerabilities within smart home systems and Artikel best practices for ensuring a secure and private smart home environment.
Smart home systems, by their very nature, collect and transmit a considerable amount of data. This data, ranging from personal schedules and preferences to biometric information and location data, represents a valuable target for malicious actors. A compromised smart home device can provide access to sensitive information, enabling identity theft, financial fraud, or even physical intrusion. Data breaches, often resulting from weak passwords, unpatched software, or vulnerabilities in the underlying network infrastructure, can expose personal information to unauthorized parties, leading to significant consequences for homeowners.
Potential Security Risks and Data Breaches
Smart home systems face various security risks, including unauthorized access to devices and networks through vulnerabilities in software or hardware, phishing attacks targeting user credentials, malware infections compromising device functionality, and denial-of-service attacks disrupting system operation. Data breaches can expose sensitive personal information such as user profiles, location data, and even biometric data collected by smart devices. For example, a vulnerability in a smart camera could allow hackers to remotely access the camera feed, compromising the homeowner’s privacy and potentially facilitating surveillance.
Similarly, a compromised smart lock could grant unauthorized access to the home. The consequences of such breaches can range from inconvenience and financial loss to significant personal safety risks.
Best Practices for Securing Smart Home Networks and Devices
Establishing a secure smart home environment requires a multi-layered approach. This includes using strong, unique passwords for each device and account; regularly updating firmware and software to patch security vulnerabilities; enabling two-factor authentication whenever possible; securing the home Wi-Fi network with a strong password and encryption (WPA2/WPA3); segmenting the smart home network from other home networks; carefully vetting third-party apps and integrations before connecting them to the smart home system; and employing robust firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Regularly reviewing and updating security settings on all devices is crucial. Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt internet traffic and protect against eavesdropping. Furthermore, understanding the data collection practices of different smart home devices and platforms is essential to making informed decisions about privacy.
Examples of Security Features Offered by Different Smart Home Platforms, Smart Home Integration
Different smart home platforms offer varying levels of security features. Amazon Alexa, for example, employs voice recognition technology with measures to prevent unauthorized activation and offers multi-factor authentication for account access. Google Home provides features like encrypted communication and regular security updates. Apple HomeKit utilizes end-to-end encryption for many of its functionalities. However, it’s crucial to remember that no system is entirely impenetrable, and maintaining a proactive security posture remains paramount.
Regular security audits and staying informed about emerging threats are essential for minimizing risks. Many platforms also offer features like activity logs, allowing users to monitor device activity and identify potential unauthorized access attempts. The specific security features available will vary depending on the platform and the individual devices used.
Future Trends in Smart Home Integration
The smart home landscape is constantly evolving, driven by rapid advancements in technology and a growing demand for seamless, intuitive home automation. Emerging technologies are poised to redefine how we interact with our homes, leading to more personalized, efficient, and secure living environments. This section explores the key technological drivers and predicted developments shaping the future of smart home integration.The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and edge computing is fundamentally altering the capabilities of smart home systems.
These technologies work in synergy to enhance responsiveness, personalization, and energy efficiency. For instance, AI-powered systems can learn user preferences and adapt accordingly, automatically adjusting lighting, temperature, and entertainment based on individual needs and routines. ML algorithms can analyze energy consumption patterns to optimize energy usage, while edge computing allows for faster processing and reduced reliance on cloud connectivity, enhancing both privacy and responsiveness.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Smart Home Integration
AI, ML, and edge computing are not just buzzwords; they are already significantly impacting the smart home market. AI enables predictive maintenance, anticipating potential issues with appliances before they occur and scheduling timely repairs. ML algorithms personalize user experiences by learning individual preferences and adapting system settings accordingly. For example, a smart thermostat might learn that a resident prefers a slightly cooler temperature in the evenings and automatically adjust accordingly.
Edge computing processes data locally, reducing latency and dependency on internet connectivity, resulting in a more reliable and responsive system. This is particularly beneficial in areas with unreliable internet access. Consider, for example, a smart security system that can continue to operate even if the internet connection is temporarily disrupted.
Evolution of Smart Home Standards and Protocols
The proliferation of smart home devices from various manufacturers has highlighted the need for interoperability. The future of smart home integration hinges on the development and adoption of robust, universal standards and protocols. While existing standards like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Matter are making progress towards greater interoperability, we can expect to see further standardization efforts, potentially leading to a more unified ecosystem where devices from different brands can seamlessly communicate and work together.
This would eliminate the current fragmentation and improve the overall user experience. One can envision a future where a single platform can control all smart home devices, regardless of the manufacturer. This improved standardization will also facilitate the development of more sophisticated and integrated applications.
Future Applications of Smart Home Integration
The potential applications of smart home integration extend far beyond convenience. Smart homes are poised to play a significant role in various sectors, improving efficiency, safety, and overall quality of life.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring systems integrated into smart homes can enable proactive healthcare management, alerting caregivers to potential health issues and facilitating timely interventions. Imagine a smart home system that automatically detects a fall and alerts emergency services.
- Energy Management: Advanced smart home systems can significantly reduce energy consumption through intelligent control of appliances and lighting. AI-powered systems can learn energy usage patterns and optimize energy distribution, minimizing waste and lowering energy bills. This could contribute significantly to reducing carbon footprints.
- Security: Smart home security systems are constantly evolving, incorporating advanced features such as facial recognition, intrusion detection, and AI-powered threat assessment. Integrated systems can provide a comprehensive and proactive security solution, enhancing safety and peace of mind. For instance, a system could automatically lock doors and activate security cameras upon detecting an unauthorized entry attempt.
Smart Home Integration Use Cases
Smart home integration goes beyond simply connecting individual devices; it’s about creating a cohesive ecosystem that enhances daily life. By integrating various systems, users unlock a level of convenience, efficiency, and security previously unimaginable. The following scenarios highlight the transformative potential of a well-integrated smart home.
Home Security Enhancement Through Integration
Smart home security systems, when fully integrated, offer a significant leap forward in protection. Imagine a system where your smart doorbell identifies an unfamiliar face, triggering an alert to your smartphone. Simultaneously, your smart lights activate, simulating occupancy, while your smart locks automatically engage. This multi-layered response, coordinated seamlessly across different devices, provides a far more robust security posture than any single component could offer. The user benefits from proactive alerts, real-time situational awareness, and a unified control interface for managing security protocols, resulting in a significantly improved sense of safety and peace of mind.
Energy Efficiency Optimization via Smart Home Integration
Energy efficiency is dramatically improved through the integration of smart thermostats, lighting, and appliances. A smart thermostat, learning your preferences and schedule, adjusts temperatures automatically to minimize energy waste. Integrated smart lighting systems respond to occupancy sensors, turning off lights in unoccupied rooms. Smart appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers, can be scheduled to run during off-peak hours, taking advantage of lower electricity rates. This holistic approach to energy management provides substantial cost savings and reduces the environmental impact of your home, demonstrating a significant return on investment and promoting sustainable living. The user experience is enhanced through automated energy optimization, leading to reduced bills and a more environmentally conscious lifestyle.
Entertainment System Integration for Enhanced User Experience
Imagine effortlessly controlling your entire entertainment system with a single voice command or a tap on your smartphone. Integrated smart home entertainment systems allow you to seamlessly switch between music, movies, and gaming, adjusting lighting and even controlling your window shades to create the perfect ambiance. Smart speakers can play your favorite playlist while your smart TV streams your preferred show, all coordinated without any manual intervention. This level of seamless control enhances the user experience, providing a more immersive and enjoyable entertainment experience. The user benefits from a more intuitive and personalized entertainment system, enhancing relaxation and leisure time.
Smart home integration offers unparalleled convenience, streamlining various household functions. A key component of this integration is often the ability to control devices using voice commands, a feature explored in detail at Voice-Controlled Home. This integration enhances the overall user experience, making smart home technology more intuitive and accessible for everyone. Ultimately, seamless voice control significantly improves the effectiveness of smart home systems.
Cost Considerations and ROI of Smart Home Integration

Source: se.com
Smart home integration offers numerous benefits, but the initial investment and ongoing costs are significant factors to consider. Understanding the cost breakdown and potential return on investment (ROI) is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will analyze the financial aspects of smart home integration, examining both the expenses and the potential long-term gains.
The cost of implementing a smart home system varies widely depending on the scope of the project, the chosen devices, and the level of professional installation required. Factors such as the size of your home, the number of devices integrated, and the complexity of the system all play a role in determining the overall expense. While some individuals opt for a DIY approach to minimize costs, others prefer the expertise of professional installers for a seamless and reliable setup.
Smart home integration offers incredible convenience, seamlessly blending technology with our living spaces. However, achieving this integration while maintaining the aesthetic appeal of, say, a Traditional Interior Design , requires careful planning and thoughtful selection of compatible smart devices. Ultimately, successful smart home integration hinges on balancing functionality with the overall design vision of your home.
Smart Home System Cost Breakdown
The following table provides a general cost estimate for various smart home components. Note that these prices are approximate and can vary based on brand, features, and retailer. Prices also fluctuate with market conditions, so it is essential to check current pricing before making any purchases.
| Component | Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Hub | $100 – $300 | The central control unit for your smart home system. Prices vary based on features and brand (e.g., Amazon Echo, Google Home, Apple HomePod). |
| Smart Lighting (per bulb) | $15 – $50 | Smart bulbs offer remote control and scheduling capabilities. Prices vary based on features like color changing and energy efficiency (e.g., Philips Hue, LIFX). |
| Smart Thermostat | $150 – $300 | Provides programmable temperature control and can learn your preferences for optimal energy efficiency (e.g., Nest, Ecobee). |
| Smart Security System (basic) | $200 – $500 | Includes sensors, cameras, and a control panel for monitoring and security alerts (e.g., Ring, SimpliSafe). Monthly monitoring fees may apply. |
| Smart Locks | $150 – $300 | Allows for keyless entry and remote locking/unlocking capabilities (e.g., August, Schlage). |
| Professional Installation (per hour) | $50 – $100 | Hiring a professional installer can simplify the setup process and ensure proper functionality. |
Return on Investment (ROI) of Smart Home Integration
While the initial investment can be substantial, smart home integration can offer a significant return on investment over time. Two primary avenues for ROI are energy savings and increased home value.
Smart home integration offers a convenient way to manage various aspects of your home, enhancing both comfort and security. A key component of this interconnected ecosystem is often smart lighting, which can significantly improve ambiance and energy efficiency. For a deeper dive into the possibilities of customized lighting solutions, check out this resource on Smart Lighting.
Ultimately, integrating smart lighting seamlessly enhances the overall experience of a connected smart home environment.
Energy Savings: Smart thermostats, for instance, can learn your heating and cooling preferences and automatically adjust temperatures when you’re away, resulting in lower energy bills. Smart lighting allows for automated switching off of lights in unoccupied rooms, further reducing energy consumption. These savings accumulate over time, potentially offsetting the initial investment. For example, a family saving $100 per year on energy bills for 10 years realizes a $1000 return.
This example assumes consistent savings, which may vary based on usage and energy prices.
Increased Home Value: Smart home features are increasingly desirable among homebuyers. Homes equipped with advanced technology, such as smart security systems and automated lighting, often command higher prices on the real estate market. The precise increase in value depends on various factors, including location, market conditions, and the specific features installed. However, studies suggest that smart home features can contribute to a noticeable increase in a property’s appraisal value, adding to the overall ROI.
Summary
Ultimately, smart home integration offers a compelling vision of the future of living, promising increased comfort, security, and efficiency. While challenges remain in areas like interoperability and security, ongoing innovation and the development of robust standards are paving the way for a more seamless and intuitive smart home experience. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for smart home integration to transform how we live, work, and interact with our homes is undeniable.
The journey towards a fully integrated and personalized smart home is ongoing, and the rewards are well worth the effort.
FAQ Resource
What are the typical upfront costs of setting up a smart home system?
The initial investment varies greatly depending on the scale and complexity of your system. A basic setup might cost a few hundred dollars, while a comprehensive system with numerous devices could cost several thousand.
How much energy can I realistically save with smart home integration?
Energy savings depend on the specific devices and their usage. Smart thermostats and lighting can yield significant reductions, often in the range of 10-20%, but individual results may vary.
Can I control my smart home devices remotely?
Yes, most smart home systems offer remote control capabilities through mobile apps or web interfaces, allowing you to manage your home from anywhere with an internet connection.
What happens if my internet connection goes down?
Functionality will vary depending on the system and device. Some devices might continue to operate in a limited capacity, while others may become completely inoperable until internet connectivity is restored.
Are smart home systems difficult to install and configure?
The complexity depends on the system and your technical skills. Some systems are designed for easy DIY installation, while others may require professional help.