Solar Power Expansion in Africa A Growing Energy Future
Solar power expansion in Africa presents a compelling narrative of potential and progress. The continent, blessed with abundant sunlight, is witnessing a surge in solar energy adoption, driven by the urgent need for reliable electricity access and the promise of economic development. This burgeoning sector faces significant challenges, including financing limitations and infrastructural hurdles, yet innovative solutions and technological advancements are paving the way for a brighter, more sustainable future powered by the sun.
This exploration delves into the current state of solar power across diverse African nations, analyzing the growth potential while acknowledging the barriers to widespread adoption. We’ll examine technological innovations, assess social and environmental impacts, and analyze the crucial role of policy and regulatory frameworks in shaping the future of solar energy on the continent. Finally, we will project the potential for solar power to contribute significantly to Africa’s energy independence and economic prosperity.
Current State of Solar Power in Africa
Africa possesses significant solar energy potential, yet its harnessing remains relatively underdeveloped compared to its vast resources. While progress is being made, challenges related to infrastructure, financing, and policy hinder wider adoption. This section details the current state of solar power across the continent, highlighting key aspects of capacity, infrastructure, and major players.
The expansion of solar power in Africa is a complex issue influenced by a multitude of factors, including geographical location, political stability, economic development, and technological advancements. The continent’s abundant sunshine offers a unique opportunity to leapfrog traditional energy infrastructure and achieve sustainable energy independence.
Solar Power Capacity and Energy Mix
Precise figures on solar power capacity vary depending on the source and reporting year. The following table provides an approximation of the current situation in select African countries. It is important to note that data collection and reporting across the continent are not always consistent, leading to discrepancies in available information.
The expansion of solar power in Africa holds immense potential for sustainable development, offering a pathway to energy independence and economic growth. This mirrors similar large-scale green energy transitions happening elsewhere, such as the significant advancements detailed in this report on Green energy initiatives in Europe. Ultimately, successful solar projects in Africa could provide valuable lessons and inspire further global investment in renewable energy sources.
| Country | Current Capacity (MW) | Percentage of Total Energy Mix | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa | 2000 (approx.) | 5% (approx.) | Grid infrastructure limitations, intermittent power supply |
| Egypt | 1500 (approx.) | 3% (approx.) | Land acquisition, financing for large-scale projects |
| Morocco | 1000 (approx.) | 7% (approx.) | Water scarcity in some CSP projects, transmission line constraints |
| Kenya | 800 (approx.) | 2% (approx.) | Decentralized nature of energy needs, high upfront costs |
| Nigeria | 500 (approx.) | 1% (approx.) | Political instability, lack of investment in grid infrastructure |
Note: These figures are estimates and may not reflect the most up-to-date information. The percentage of the total energy mix varies significantly depending on the country’s overall energy consumption and generation capacity.
Solar Power Infrastructure and Technologies
Africa utilizes a range of solar technologies, predominantly photovoltaic (PV) systems due to their relative affordability and ease of deployment. These systems range from small-scale rooftop installations to large-scale utility-connected solar farms. Concentrated solar power (CSP) technology, which uses mirrors to focus sunlight and generate heat, is also being explored in several countries, particularly those with high solar irradiance and suitable land availability.
However, CSP projects tend to be more capital-intensive and require significant land areas.
Major Players in the African Solar Power Sector
The African solar power sector involves a diverse range of actors, including multinational corporations, local companies, governments, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). Some key players include:
- International Companies: Companies like EDF Renewables, Engie, and TotalEnergies are actively involved in large-scale solar projects across the continent.
- Local Companies: Numerous local companies are emerging as key players in the development and implementation of smaller-scale solar projects, often focusing on off-grid solutions.
- Governments: Several African governments are actively promoting solar power development through policy initiatives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks. Examples include Morocco’s Noor solar complex and Kenya’s efforts to expand off-grid solar access.
- NGOs: Organizations like the World Bank, the African Development Bank, and various international NGOs are providing funding and technical support for solar projects, often focusing on community-based initiatives and rural electrification.
Growth Potential and Barriers: Solar Power Expansion In Africa
Africa possesses immense potential for solar power expansion, driven by a confluence of factors promising significant economic and social benefits. This potential, however, is significantly hampered by various challenges that require innovative solutions and concerted efforts from governments, private investors, and international organizations.
Factors Driving Solar Power Expansion
Africa’s abundant sunshine provides a readily available and sustainable energy source. This is particularly crucial given the continent’s rapidly growing energy demand fueled by increasing population and industrialization. Many regions lack access to reliable electricity grids, making decentralized solar power solutions particularly attractive. The economic benefits are substantial, including job creation in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, as well as reduced reliance on expensive and polluting fossil fuels.
The potential for rural electrification and improved living standards through access to clean energy further strengthens the case for solar power expansion. For example, successful solar mini-grid projects in Kenya have demonstrated the viability of providing electricity to remote communities, improving healthcare, education, and economic opportunities.
Barriers Hindering Solar Power Expansion
Significant barriers impede the rapid expansion of solar power in Africa. Financing remains a major constraint, with high upfront capital costs presenting a challenge for both governments and private developers. The lack of robust and reliable grid infrastructure limits the ability to integrate large-scale solar power plants into national grids, necessitating costly grid upgrades or off-grid solutions. Policy and regulatory uncertainties, including inconsistent permitting processes, unclear land ownership rights, and inadequate feed-in tariffs, create an unstable investment environment.
Furthermore, a lack of skilled workforce and technological expertise can hinder project implementation and maintenance. For instance, the inconsistent application of regulations across different African countries creates uncertainty for investors, discouraging large-scale investments.
Regional Variations in the Solar Energy Landscape
The solar energy landscape varies considerably across different regions of Africa. North Africa, with its vast deserts and high solar irradiance, has significant potential for large-scale solar power plants, often connected to national grids or exported to Europe via undersea cables. Sub-Saharan Africa, on the other hand, faces more challenges due to dispersed populations, weaker grid infrastructure, and higher reliance on off-grid solutions like mini-grids and standalone systems.
While North Africa might leverage its geographical advantage to attract large-scale investments, Sub-Saharan Africa needs a focus on decentralized solutions to address its unique energy access challenges. The success of Morocco’s Noor Ouarzazate solar complex, one of the world’s largest concentrated solar power plants, contrasts with the diverse approaches needed for off-grid electrification in rural communities across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Potential Solutions to Address Financing Barriers
Addressing the financing gap is crucial for accelerating solar power expansion. Several solutions can be implemented:
The following points highlight potential solutions to overcome the financing challenges faced by solar power projects in Africa:
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Leveraging the financial strength of both public and private sectors to share risks and reduce financial burdens.
- Concessional Financing: Utilizing low-interest loans and grants from international development institutions like the World Bank and the African Development Bank.
- Green Bonds and Climate Finance: Mobilizing private investment through green bonds and accessing climate funds dedicated to renewable energy projects.
- Risk Mitigation Instruments: Implementing risk mitigation tools like guarantees and insurance to attract private investment.
- Pay-As-You-Go (PAYGo) Financing Models: Enabling access to solar home systems through affordable installment plans.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The rapid advancement of solar technology is proving crucial for expanding solar power access across Africa. This progress encompasses not only the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar panels but also the development of innovative solutions tailored to the continent’s unique energy needs and infrastructure challenges. These advancements are complemented by the emergence of creative financing models that are vital in overcoming financial hurdles and accelerating deployment.Recent technological advancements are directly addressing Africa’s energy poverty.
The focus is on decentralized, off-grid solutions that bypass the limitations of existing power grids. This shift allows for rapid deployment and greater reach in remote and underserved communities.
Off-Grid and Mini-Grid Solutions
Off-grid solar systems, utilizing standalone photovoltaic (PV) panels and batteries, provide electricity to individual households and small businesses. Mini-grids, on the other hand, serve larger communities by connecting multiple households and businesses to a localized network of solar panels, batteries, and sometimes, generators for backup power. The increasing affordability and efficiency of these systems, combined with advancements in battery technology, are making them increasingly viable and attractive options.
For instance, improvements in battery storage capacity and lifespan are reducing the reliance on expensive and often unreliable diesel generators, a common feature in many mini-grid solutions.
Innovative Financing Mechanisms
Securing funding for solar projects in Africa often presents a significant challenge. However, innovative financing mechanisms are playing a crucial role in bridging this gap. Crowdfunding platforms allow for direct investment from individuals and organizations, fostering community ownership and participation. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) combine the resources and expertise of governments and private sector companies, leveraging both public funds and private investment to finance large-scale projects.
These partnerships often include risk-sharing agreements and performance-based incentives, ensuring project sustainability. Pay-as-you-go (PAYGo) financing models, where customers make small, regular payments for solar home systems, are also gaining popularity, making solar energy accessible to low-income households.
Successful Solar Energy Projects in Africa
Several successful solar projects in Africa showcase the effectiveness of these technological advancements and innovative financing mechanisms.
| Project Name | Location | Technology Used | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kipeto Wind Farm | Kenya | Hybrid wind and solar power generation | Provides clean energy to the national grid, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. |
| Noor Ouarzazate Solar Power Station | Morocco | Concentrated solar power (CSP) | One of the largest CSP plants globally, contributing significantly to Morocco’s renewable energy goals. |
| Scaling Solar | Zambia | Solar PV mini-grids and PAYGo financing | Provides reliable electricity to rural communities, improving livelihoods and economic opportunities. |
| Azuri Technologies | Multiple African countries | Off-grid solar home systems with PAYGo financing | Provides affordable solar energy access to millions of households in off-grid areas. |
Social and Environmental Impacts
The expansion of solar power in Africa presents a complex interplay of social and environmental consequences. While offering immense potential for development, careful consideration of potential negative impacts and proactive mitigation strategies are crucial to ensure sustainable and equitable growth. This section explores the multifaceted effects of solar energy deployment, highlighting both the benefits and challenges.
The social and environmental implications of expanding solar power in Africa are intrinsically linked. A successful transition requires a balanced approach that prioritizes both economic development and environmental protection. Failure to address potential negative impacts could undermine the long-term benefits of solar energy adoption.
Social Benefits of Solar Power Expansion
Expanding solar power across Africa offers significant social advantages. Increased access to electricity empowers communities, fostering economic growth and improving quality of life. Job creation in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and associated industries stimulates local economies. Furthermore, improved healthcare through reliable electricity supply and enhanced educational opportunities via access to technology contribute to human development. For example, the increased availability of electricity in rural communities has enabled the operation of small businesses, leading to increased income and employment opportunities.
The improved lighting provided by solar power also contributes to safer environments, reducing accidents and improving overall well-being.
Environmental Implications of Large-Scale Solar Power Development
While a cleaner energy source than fossil fuels, large-scale solar power development does present environmental challenges. Significant land areas are required for solar farms, potentially impacting natural habitats and biodiversity. The manufacturing process of solar panels involves the use of materials that can be harmful to the environment if not properly managed. Finally, the disposal of end-of-life solar panels presents a waste management challenge requiring careful consideration.
For instance, the construction of large solar farms in arid and semi-arid regions can lead to habitat fragmentation and displacement of wildlife. The extraction of raw materials for panel production can also contribute to environmental degradation if not carried out sustainably.
Mitigation Strategy for Negative Environmental Impacts
A comprehensive strategy is needed to mitigate the potential negative environmental impacts of solar power expansion. This strategy should incorporate the following key elements:
Careful site selection is paramount to minimize impacts on sensitive ecosystems. Environmental impact assessments should be conducted prior to the development of any solar project to identify and address potential risks.
- Prioritize the development of solar projects on degraded or already disturbed land to minimize habitat loss.
- Implement robust environmental monitoring programs to track the impact of solar farms on biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Develop and implement effective waste management strategies for the disposal of end-of-life solar panels, including recycling and responsible disposal of hazardous materials.
- Promote the use of environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing processes in the production of solar panels.
- Collaborate with local communities to ensure that solar power development is socially and environmentally responsible.
- Invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and sustainability of solar technologies.
Contribution of Solar Power to Sustainable Development Goals
Solar power expansion aligns significantly with several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It contributes directly to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) by providing access to electricity for millions across Africa. The creation of jobs and improved economic opportunities contribute to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). Improved health outcomes and educational opportunities linked to increased energy access support SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 4 (Quality Education).
Finally, responsible development of solar power projects can contribute to SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 15 (Life on Land) through mitigation of climate change and protection of biodiversity. The expansion of solar energy in rural areas, for example, can improve access to healthcare and education, directly contributing to improved health and educational outcomes. This exemplifies the potential of solar power to act as a catalyst for broader sustainable development.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
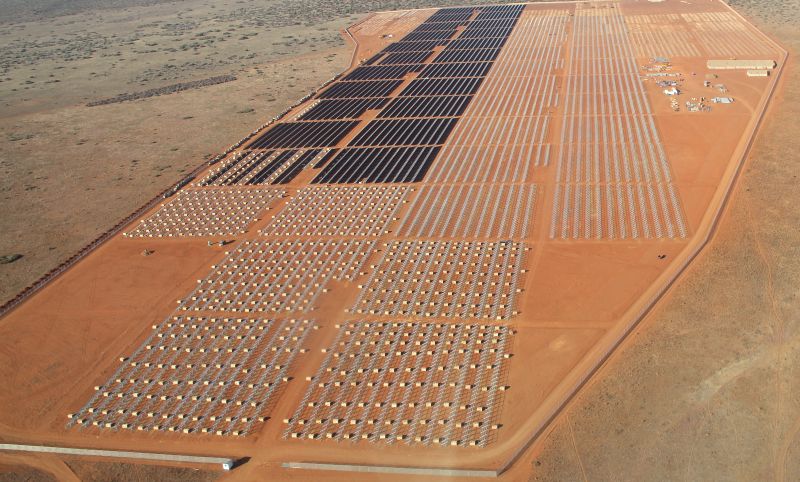

Source: cnn.com
The effectiveness of solar power expansion in Africa is heavily reliant on supportive and well-structured policy and regulatory frameworks. These frameworks shape investor confidence, streamline project development, and ensure the sustainable integration of solar energy into national grids. A lack of clear policies can hinder investment, create uncertainty, and ultimately slow down the much-needed energy transition. This section will analyze existing policies in selected African countries, identify best practices, and offer key recommendations for accelerating solar power expansion.Existing policies and regulations related to solar power development vary significantly across African nations.
Some countries, such as South Africa and Kenya, have established relatively comprehensive regulatory frameworks, including feed-in tariffs, licensing procedures, and grid connection standards. These frameworks, while not perfect, have attracted substantial investment in solar power projects. Conversely, other countries face challenges such as inconsistent policies, bureaucratic hurdles, and a lack of transparent regulatory processes, resulting in limited private sector participation.
For instance, some countries lack clear guidelines on land acquisition for solar projects, leading to delays and disputes. The complexity of navigating different regulatory bodies further adds to the challenges faced by developers.
Regulatory Best Practices for Solar Power Investment
Effective policy design is crucial for attracting investment and accelerating solar power deployment. Best practices include establishing clear and stable regulatory frameworks, simplifying permitting processes, and guaranteeing fair and predictable returns on investment. This requires a coordinated effort among government agencies, involving the ministries of energy, finance, and environment. Transparency is also paramount, ensuring clear communication and accessible information to investors regarding regulatory requirements and incentives.
Several countries have successfully implemented feed-in tariffs, which guarantee a minimum price for solar power sold to the grid, providing a stable revenue stream for investors. Kenya, for example, has utilized feed-in tariffs to stimulate the growth of its solar power sector. Another effective strategy is the use of public-private partnerships (PPPs), which combine the resources and expertise of both the public and private sectors to develop large-scale solar projects.
These partnerships help to mitigate risk and ensure efficient project implementation. Countries such as Morocco have successfully utilized PPPs to develop significant solar power capacity.
Key Policy Recommendations for Accelerating Solar Power Expansion in Africa
A coordinated and comprehensive approach is essential to accelerate solar power expansion across the continent. The following policy recommendations are critical for creating a supportive environment for solar energy development:
- Standardize and Simplify Permitting Processes: Streamline bureaucratic procedures and establish a single window for project approvals to reduce delays and costs.
- Implement Competitive Bidding Processes: Encourage transparency and efficiency in project selection through transparent and competitive bidding processes.
- Guarantee Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Provide long-term PPAs with clear pricing mechanisms to assure investors of stable revenue streams.
- Develop Clear Grid Connection Policies: Establish clear guidelines and standards for grid connection to facilitate the integration of solar power into national grids.
- Invest in Grid Infrastructure: Upgrade existing grid infrastructure to accommodate the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources, including solar power.
- Promote Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Leverage the expertise and resources of the private sector through well-structured PPPs to accelerate project development.
- Foster Capacity Building: Invest in training and education programs to develop a skilled workforce capable of supporting the solar power sector.
- Establish Clear Land Tenure Policies: Develop clear guidelines and processes for land acquisition to avoid delays and disputes related to solar project development.
- Incentivize Local Content and Manufacturing: Promote the use of locally sourced materials and equipment to stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
Future Outlook and Projections
The expansion of solar power in Africa presents a compelling narrative of potential and progress. Over the next decade, the continent is poised for significant growth in its renewable energy sector, with solar power at the forefront. This growth will be driven by a confluence of factors, including decreasing technology costs, supportive government policies, and a growing recognition of solar’s crucial role in achieving sustainable development goals.The potential for solar power to transform Africa’s energy landscape and drive economic growth is immense.
Africa’s burgeoning solar power sector is rapidly transforming energy access and fostering economic development. This expansion is a prime example of how green energy initiatives are creating jobs and stimulating growth, as detailed in this insightful article: How green energy is driving economic growth. Consequently, increased solar power capacity in Africa is not only brightening homes but also bolstering entire economies.
Meeting the continent’s growing energy demands while mitigating climate change requires a rapid transition to cleaner energy sources, and solar offers a viable and scalable solution. This transition will not only improve access to electricity for millions but also stimulate economic activity through job creation, infrastructure development, and increased agricultural productivity.
Africa’s solar power expansion is rapidly accelerating, driven by the continent’s abundant sunshine and growing energy demands. To understand the key players facilitating this growth, it’s helpful to consult resources like this list of Top green energy companies to watch in 2025 , many of whom are heavily invested in African solar projects. This influx of investment and technological expertise is crucial for ensuring the sustainable development of solar energy across the continent.
Projected Solar Power Capacity Expansion
Several organizations, including the International Energy Agency (IEA) and IRENA (International Renewable Energy Agency), project significant increases in Africa’s solar power capacity over the next 5-10 years. These projections often vary based on differing assumptions about policy support, investment levels, and technological advancements. However, a common thread is the expectation of substantial growth. For instance, the IEA’s World Energy Outlook often projects a doubling or even tripling of solar capacity in key African nations within the next decade, depending on the scenario considered.
This growth would involve large-scale solar farms, as well as a proliferation of smaller-scale installations for both residential and commercial use. Examples of countries already showing rapid growth include South Africa, Morocco, and Kenya, which are attracting significant investments in solar energy projects. The success of these initiatives often serves as a catalyst for expansion in neighboring countries.
Solar Power’s Role in Energy Independence and Economic Growth
Achieving energy independence is a crucial element of Africa’s development agenda. Over-reliance on imported fossil fuels creates vulnerabilities to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability. Solar power, being a domestically sourced energy resource, offers a pathway to greater energy security and self-sufficiency. This energy independence translates directly into economic growth. The increased access to electricity facilitates industrialization, improves agricultural productivity, and enhances the quality of life for individuals and communities.
Furthermore, the solar energy sector itself creates numerous jobs, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation, boosting local economies and fostering entrepreneurship. For example, the growth of solar-powered irrigation systems can significantly increase agricultural yields, improving food security and generating income for farmers.
A Hypothetical Successful Future Scenario, Solar power expansion in Africa
Imagine Africa in 2035. Vast solar farms, shimmering under the abundant sunshine, dot the landscapes of numerous countries. Advanced energy storage technologies, such as large-scale battery systems and pumped hydro storage, ensure a reliable and consistent supply of electricity, even during periods of low solar irradiance. Smart grids, leveraging sophisticated digital technologies, optimize energy distribution and minimize transmission losses.
Solar power expansion in Africa holds immense potential, but intermittent sunlight necessitates effective energy storage. Addressing this challenge requires advancements like those detailed in this insightful article on Innovations in green energy storage systems. Ultimately, reliable storage solutions are key to unlocking the full benefits of solar energy across the continent and ensuring consistent power supply.
Decentralized solar microgrids power remote communities, previously unconnected to the national grid, bringing electricity to schools, hospitals, and homes. The continent’s industries thrive on clean, affordable energy, creating millions of high-skilled jobs in the renewable energy sector and related industries. A vibrant ecosystem of solar entrepreneurs, innovators, and researchers drives continuous technological advancements and fuels sustainable economic growth.
Access to clean energy has transformed lives, improving health outcomes, educational opportunities, and overall quality of life for millions of Africans. This future is not a utopian dream; it’s a realistic possibility if the current momentum towards solar energy expansion is sustained and amplified.
Final Review
The expansion of solar power in Africa is not merely an energy transition; it’s a transformative journey. While challenges remain, the potential benefits—from enhanced energy access and economic growth to environmental sustainability and improved quality of life—are undeniable. Through innovative technologies, strategic partnerships, supportive policies, and a commitment to sustainable practices, Africa can harness the power of the sun to illuminate a path towards a brighter, more prosperous future for all its citizens.
The journey will require continued investment, collaboration, and a shared vision, but the potential rewards are immense and worth pursuing.
Questions Often Asked
What are the most common types of solar technologies used in Africa?
Photovoltaic (PV) systems are most prevalent, followed by concentrated solar power (CSP) in regions with high solar irradiance. Off-grid and mini-grid solutions are also gaining traction.
How does solar power contribute to sustainable development goals in Africa?
Solar energy directly supports several SDGs, including affordable and clean energy (SDG 7), climate action (SDG 13), and industry, innovation, and infrastructure (SDG 9), by providing clean energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and stimulating economic growth.
What are the potential risks associated with large-scale solar projects?
Potential risks include land use conflicts, habitat disruption, and the need for responsible waste management of solar panels at the end of their lifecycle. Careful planning and mitigation strategies are crucial.
What role do international organizations play in supporting solar power development in Africa?
Organizations like the World Bank, the African Development Bank, and various NGOs provide funding, technical assistance, and policy support to accelerate solar energy deployment across the continent.